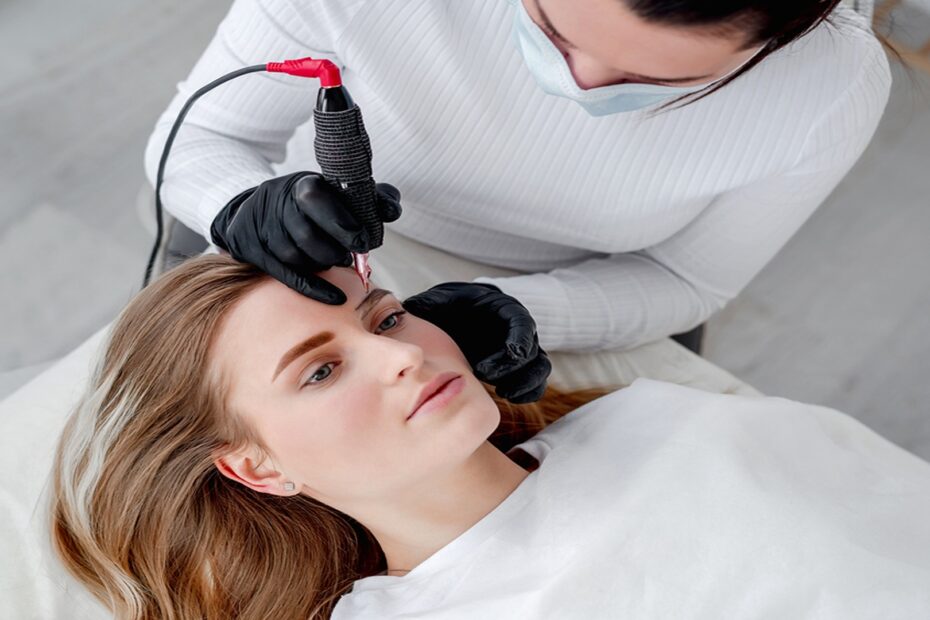
What is microblading?
Microblading is a popular cosmetic procedure that involves the use of a hand-held tool with small needles to deposit pigment into the skin, creating hair-like strokes that mimic natural eyebrows. But how does this technique work.
How does microblading work?
- It uses a hand-held tool with small needles to create tiny incisions in the skin.
- The pigment is then deposited into the incisions to create the appearance of hair-like strokes that mimic natural eyebrow hairs.
- The technique involves using the needles at a specific angle and depth to achieve the desired effect.
What is the process of microblading?
- The procedure typically takes around two hours to complete.
- Before the procedure, a numbing cream is applied to the treatment area to minimize discomfort.
- The technician uses a pen to draw the desired eyebrow shape onto the skin.
- Once the shape is approved, the technician uses the microblading tool to create the hair-like strokes.
- After the initial appointment, a touch-up appointment may be necessary to achieve the desired result.
How long do the results of microblading last?
- With proper aftercare, the results of this can last up to three years.
- After the procedure, it is important to follow the technician’s instructions for aftercare, such as avoiding getting the area wet and applying a healing ointment.
Is microblading safe?
- This is generally considered safe when performed by a trained and experienced technician.
- However, there is a risk of infection and other complications if proper hygiene and safety protocols are not followed.
Conclusion
Microblading is a cosmetic technique that creates natural-looking eyebrows by depositing pigment into the skin. The technique involves using a hand-held tool with small needles to create hair-like strokes that mimic natural eyebrow hairs. With proper aftercare, the results of it can last up to three years. While this is generally considered safe, it is important to choose a reputable technician and follow proper aftercare instructions to minimize the risk of complications.